Manufacturers of sterile and non-sterile products are facing a significant challenge with the new Annex 1 EU GMP. The Annex serves as a valuable reminder that proper management of the Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) is necessary to achieve better contamination control of final products. It is imperative that manufacturers plan and structure their activities effectively to achieve the new objectives optimally. The success of any improvement project rests on proper planning.
How to Plan and structure activities for Annex 1 EU GMP compliance
- Assemble a team of multidisciplinary experts. Establish a competent team and effective communication methods from the beginning of the project. Involve all parties and departments such as microbiology, production, quality assurance, quality control, validation, regulatory affairs, etc. At this stage, it is imperative to observe processes to determine the initial scopes and responsibilities.
- Assess the level of contamination control maturity, i.e., whether there is extensive experience in the manufacturing of sterile drugs or other products where contamination control is essential.
- Gather relevant data. Collectively manage knowledge and update information contained in documents and databases. Gather all technical information about the product and the process and utilizing internal documentation to ensure effective contamination control.
- Perform a gap assessment for the required changes in Annex 1 EU GMP. A gap analysis will help you understand the extent of the difference between the current situation and the one defined by Annex 1.
- Pay attention to the design and control of facilities, equipment, services, and processes. Evaluating the facility and process design (including the integration of new advanced manufacturing technologies, barrier systems -RABS, isolators- and new monitoring/control methodologies) and reviewing the status of qualification/validation are crucial to ensure that current practices meet the new requirements.
- Focus on personnel. Specific training in contamination matters (e.g., gowning, hygiene, aseptic, disinfection, and cleaning practices) is necessary, as well as personnel qualification and disqualification requirements.
- Collaborate with expert suppliers. Engaging expert suppliers provides greater assurance for all stages of the manufacturing process and the supply chain. Their assessment and the development of specific quality agreements are critical considerations.
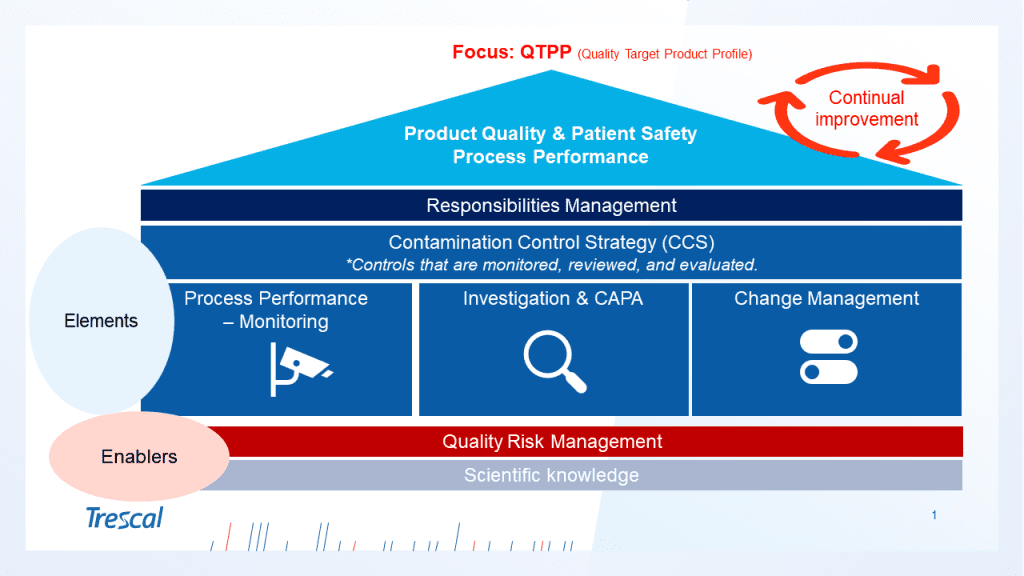
- Effective PQS and close the CCS (Contamination Control Strategy) policy. The CCS should align with the PQS for a holistic assessment of risks and existing containment measures. Assessing the impact of Annex 1 changes on defined CCS aspects should involve continuous periodic review of the PQS. Continuous analysis of data and trends is important for establishing timely improvement and mitigation plans. The availability of robust advanced analysis and investigation tools plays a significant role here.
- Robust Quality Risk Management (QRM) system. Having a robust quality risk management system is crucial for effective risk-based decision-making. It is important to have the appropriate data and to select the risk management tool and the level of formality of the QRM process that best fits each project stage based on the level of uncertainty, complexity, and importance.
Contamination control strategy and PQS
Manufacturers must adopt a risk-based approach to assess their current processes and facilities to determine the most effective measures required to meet the new Annex 1 requirements and thereby enhance their PQS in terms of contamination control and prevention. And all this, on the basis of a periodic and continuous review.
The Trescal advantage
Trescal is a global service provider for the Life Science industry, offering documented evidence that you meet internal standards, GxP guidelines and regulatory compliance. Our single source solution provides precision expertise in every service, geography and instrument across the world.




